In today’s data-driven world, safeguarding sensitive information is more critical than ever. Data Security Posture Management (DSPM) offers organizations a proactive way to monitor, manage, and secure their data environments. This article delves into the fundamentals of DSPM, differentiating between active and passive approaches, and explores how integrations between the two can enhance these strategies. Finally, we’ll highlight how Privacera’s solutions in these areas can elevate your DSPM efforts, ensuring comprehensive data discovery and protection across your organization.
Overview of DSPM
Data Security Posture Management (DSPM) is gaining traction as a solution for organizations seeking to safeguard their structured and unstructured data across their cloud platforms. By providing a holistic view of data assets, DSPM equips security and risk management professionals with the data needed to identify and mitigate privacy and security threats as data flows through complex pipelines and crosses international borders. This proactive approach is increasingly essential in a landscape where data is widely distributed and more susceptible to security breaches, emphasizing the need for a comprehensive data protection strategy.
Several factors underscore the growing relevance of DSPM, such as the rapid expansion of data across cloud environments and the tightening regulatory frameworks, including the recent SEC mandate on reporting material cybersecurity incidents. DSPM solutions leverage data lineage analysis, integration with identity and access management (IAM) systems, and real-time alert mechanisms to offer a nuanced understanding of an organization’s data security posture. These capabilities not only identify hidden data repositories but also play a crucial role in assessing and managing risks related to data residency, privacy, and security.
What is Passive DSPM?
Passive or static Data Security Posture Management (DSPM) focuses on the discovery and assessment of data risks without actively intervening to remediate them. Passive DSPM’s primary function is to map out data repositories across cloud infrastructures, identifying where sensitive data resides and highlighting potential access vulnerabilities. By creating detailed data maps and analyzing data flows and pipelines, passive DSPM uncovers shadow data stores, misconfigurations, and inconsistencies in security controls, providing a clear view of where data risks exist.
Passive DSPM tools also examine data lineage and access patterns, continuously assessing the sensitivity, residency, and accessibility of data across both structured and unstructured pipelines. This analysis is crucial for understanding how data moves and is used within an organization, ensuring that it aligns with security policies and business objectives. Additionally, these tools identify specific data risks by mapping which user accounts have access to sensitive datasets, offering a top-down view of data security across interconnected pipelines.
However, passive DSPM stops short of automating any corrective actions. Numerous point static DSPM solutions have come to the market recently that mainly focus on this first part of the lifecycle, and while they generate alerts and provide valuable insights into data security risks, they rely on manual interventions to address issues that are discovered and can result in security incidents. Security teams must manually act on the insights provided, requesting protections or access management to mitigate identified risks. This lack of automation means that while passive DSPM is excellent at highlighting where data risk lives, it requires human oversight and action to ensure those risks are addressed.
We will add FAQ Schema behind this question/answer to which will allow for this answer to show up in People Also Ask
What is Active DSPM?
Active DSPM enables organizations to not only identify but mitigate, secure, and monitor data risks in real-time or at minimum in a single integrated platform. While passive DSPM, which focuses on discovery and assessment, active DSPM adds the ability to apply automated policies and sensitivity tags to enforce data security controls across an organization’s data landscape. This approach ensures continuous governance, simplifying the management of expanding data estates and enhancing compliance through transparency, consistency, and auditability.
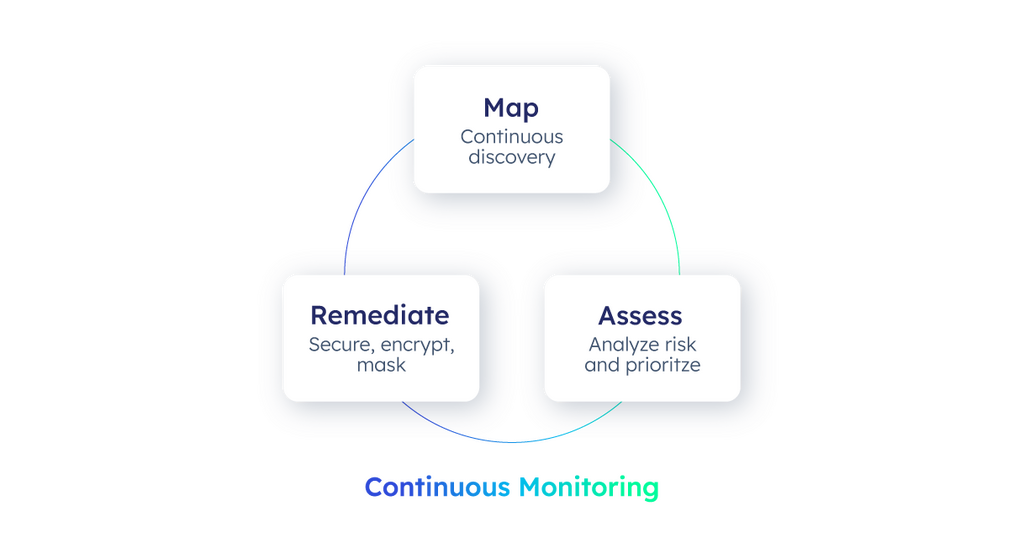
Active DSPM operates in three main steps:
- Map: It begins with enterprise-grade sensitive data discovery, classification, and tagging, providing a visual map of where sensitive data resides, who has access, and the associated business risks.
- Assess: The next step involves assessing the risk impact by analyzing access patterns, over-provisioning, and creating risk-based scores to identify potential vulnerabilities.
- Remediate: Finally, active DSPM automates the enforcement of fine-grained access controls, such as role-based (RBAC), attribute-based (ABAC), and time-based access controls (TBAC), along with data masking and encryption. This automation ensures that data security measures are dynamically adjusted in response to emerging threats, with real-time monitoring and auditing offering a detailed log of data access events, enhancing overall security and governance.
This proactive approach not only strengthens data protection but also streamlines administrative tasks, making it a crucial component of modern data security strategies.
- We will add FAQ Schema behind this question/answer to which will allow for this answer to show up in People Also Ask
What are the differences between Passive and Active DSPM?
The primary difference between active and passive DSPM lies in their scope of functionality. Passive DSPM focuses on mapping and assessing data security by discovering, classifying, and visualizing sensitive data across an organization’s data estate. It provides insights into where sensitive data resides and potential risks associated with data access but stops short of taking action to mitigate them.
Active DSPM, on the other hand, extends beyond discovery and assessment by adding automated compliance workflows and fine-grained access controls. It enables organizations to automatically adjust or remove data access based on predefined policies, access controls, and implement data masking and encryption. Active DSPM is ideal for organizations that require real-time data protection, continuous monitoring, and the ability to respond quickly to emerging threats.
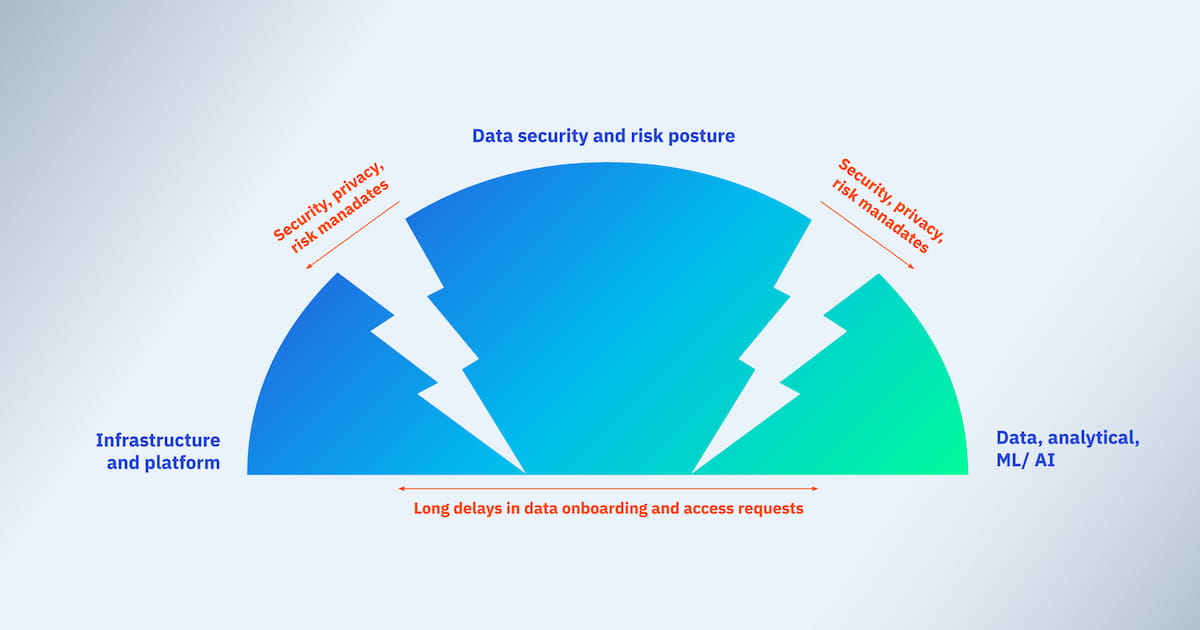
Active DSPM – The common system of record for security, infrastructure and analytical teams
The gap that exists between passive DSPM and observed risks and the subsequent remediation of those risks are at the heart of a major cause of friction in organizations. Typically, the security team defines the policies and mandates as it relates to data usage. These policy documents are then shared to the data or infrastructure teams that are charged with operating the data platform(s). This infra_data team now is caught between a rock and a hard place – on one side the security mandates and on the other the business demand for more and faster data. And our data team now needs to make a very important tradeoff – do we lock everything down or do we open it all up and let everyone get access.
Active DSPM that essentially integrates DSPM with a powerful data access security solution should now become the common system of record for all these groups.
- Security should have a live view into the system of record to understand the posture at any point in time, its changes over time.
- Data or infrastructure teams should be able to rapidly, and in most cases, in an automated way define policy instructions and controls centrally in the system and allow the system to automate the insertion of the controls into each underlying database to execute the security mandate in real time. On top of that, the system should allow for fine grained, role/ attribute or tag-based controls to enable very granular access patterns.
- The business and analytical teams should be able to manage their own data domains, manage and approve access or sharing requests and these routed and automated in the system.
Integration of Both Active and Passive DSPM
Combining active and passive Data Security Posture Management (DSPM) approaches can significantly enhance an organization’s data security practices by creating a comprehensive, proactive defense strategy. Initially, organizations may utilize passive DSPM for mapping and assessing data risks, providing visibility into where sensitive data resides and identifying potential vulnerabilities. Active DSPM then takes this a step further by automating remediation through fine-grained access controls, encryption, and masking, ensuring that identified risks are promptly mitigated.
High-level use cases for this dual approach include continuous monitoring of data access, automated policy enforcement, and streamlined incident response. By integrating these systems, organizations can move from simply understanding their security posture to actively managing and improving it in real-time. For organizations considering this approach, the process typically starts with sharing information between passive and active DSPM systems, enabling coordinated efforts between security teams and data governance personnel. The next step involves pushing workflows between DSPM and Data Security Governance platforms, allowing direct remediation of identified risks. Ultimately, the goal is to have these systems function as one, empowering CISOs with data governance leaders to invoke access and data protection actions seamlessly from the discovery of an issue through to resolution, significantly strengthening overall data security governance.
Let Privacera Help
Combining passive and active DSPM strategies offers a comprehensive approach to data security, enabling organizations to not only identify risks but also to actively manage and mitigate them. By integrating these systems, organizations create a seamless defense that continuously monitors, assesses, and protects your data assets. To delve deeper into DSPM, check out our blog, “What is DSPM?” and explore “Activating Data Security Posture Management” to discover how Posture Management helps detect inappropriate data use, assess corporate security posture, and work in harmony with Data Security Governance for a robust active posture management solution.