As organizations generate and store increasing volumes of data, implementing a data security governance (DSG) strategy has become critical for safeguarding sensitive information, ensuring compliance, and enabling strategic decision-making. This blog explores how to implement data governance effectively, from defining core principles to building a robust framework with tools like Privacera.
STEP 1: Understand the Fundamentals of Data Security Governance (DSG)
Data security governance is the practice of establishing policies, processes, and controls to manage and secure organizational data effectively. It encompasses data privacy, regulatory compliance, and risk mitigation.
STEP 2: Lay the Groundwork for DSG Implementation
Establishing a strong foundation is essential for successful DSG implementation. This involves assembling the right team, defining clear objectives, and auditing your existing infrastructure. Expectations and final outcomes should be decided and properly documented at the beginning of the project.
Creating a Cross-Functional Team
A successful DSG program requires collaboration between business and technical teams. A cross-functional team might include:
- CISOs or data protection officers to oversee governance policies.
- Governance team to define taxonomy standards and establish data security standards.
- Data stewards and business analysts to align objectives with business needs. Data stewards will also apply taxonomy standards as data classifications in a data catalog.
- IT administrators and engineers from the platform team to implement and manage technical controls, implementing access management and data masking or encryption based upon security standards.
Establish Data Security Governance Objectives
Define clear goals to align DSG efforts with organizational priorities:
- Identify business objectives, such as enhancing customer trust or achieving regulatory compliance.
- Establish key performance indicators (KPIs), like reducing the number of unauthorized data access attempts or improving response times to access requests.
- Ensure risk management and threat mitigation by identifying sensitive data and monitoring usage patterns of this data.
- Minimize the number of access management policies and provide automation to reduce the risk of human error.
Audit Existing Infrastructure
Conduct a thorough review of your data ecosystem to identify risks, gaps, and to create necessary controls:
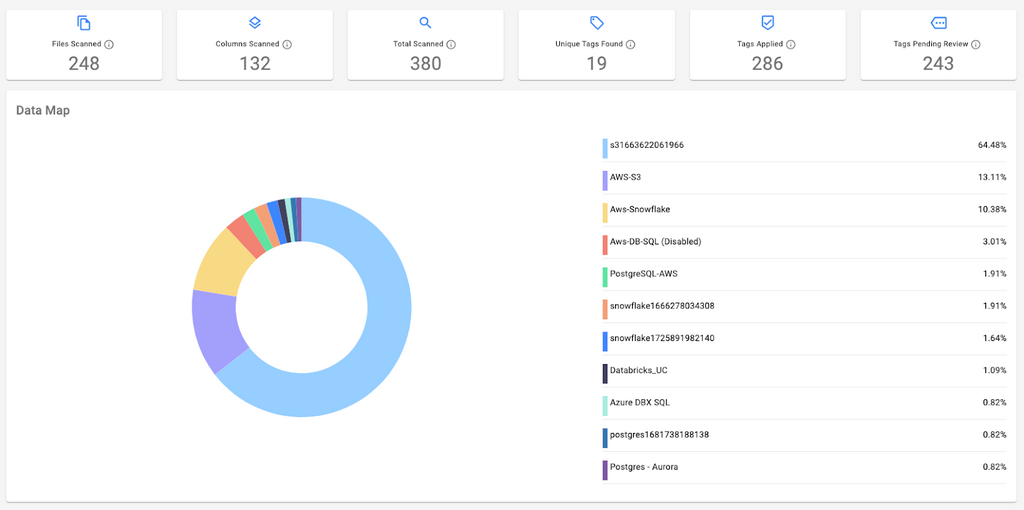
- Catalog Data Assets – Identify all structured and unstructured data sources.
- Classify Data – Categorize data based on sensitivity.
- Map Data Flow – Document how data is created, stored, accessed, shared, and disposed of across systems and teams.
- Identify Shadow IT – Detect unauthorized or ungoverned data sources used by employees or teams.
STEP 3: Identify Key Components of a Robust DSG Program
A successful DSG program integrates key policies, tools, and practices to manage and secure data effectively. An organization must understand where their sensitive data resides and be able to secure this sensitive data throughout its lifecycle.
Policy Development and Enforcement
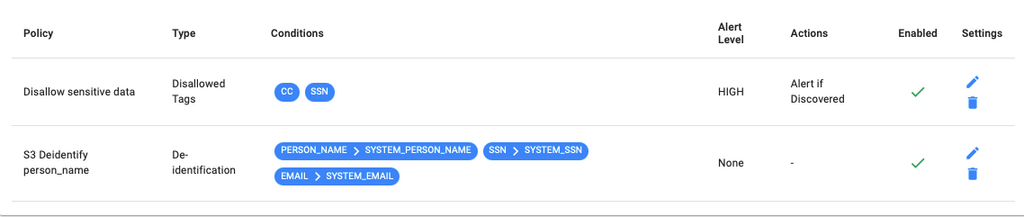
Develop comprehensive policies for data access and usage:
- Define who can access specific data and under what conditions.
- Define business level classifications based upon level of risk.
- Ensure stakeholders with a clear understanding of the data are engaged.
- Leverage governance security tools, like Privacera’s Access Management, to automate enforcement and minimize human error.
Data Classification and Cataloging
Efficient DSG starts with understanding your data:
- Use automated tools to classify sensitive and non-sensitive data.
- Build a data catalog to improve visibility and accessibility for authorized users.
- Accurately map data classifications as defined by enterprise policies to the data resources.
- Engage the proper data stewards who understand your data.
- Ensure to capture classifications with data lineage.
Access Control Management
Implement robust access controls to minimize risks:
- Use role-based access control (RBAC) and attribute-based access control (ABAC) to restrict data access based on roles or attributes.
- Configure least privilege access to ensure users have only the access they need.
- Access control should be tightly coupled with data classifications to minimize access control policies and adhere to governance standards.
Monitoring and Auditing Mechanisms
Proactively monitor and audit data access:
- Enable logging to track who accesses data and how it is used.
- Configure alerting to send notifications when unusual access patterns are observed.
- Use data classifications in reporting to identify frequency of access to highly sensitive data.
- Conduct reviews to ensure that access is not over provisioned.
STEP 4: Technical Design and Implementation
Technical considerations play a vital role in DSG implementation. Planning should be done to ensure scalability, reduce human error, and minimize user impact. This section explores how to integrate tools and automate key processes.
Building a Scalable Architecture for DSG
Design an architecture that supports scalability and flexibility:
- Integrate DSG tools into your data ecosystem, whether it’s cloud-based, on-premises, or hybrid.
- Data classification is paramount; select a data catalog to manage data classification.
- Select tools like Privacera to streamline automation and policy management.
- Ensure policy enforcement utilizes native capabilities.
- Avoid proxies to ensure query performance is not impacted.
- Design your architecture for fault tolerance and resilience with no single point of failure.
- Future proof your environment; choose tools that will allow easy integration with future architecture decisions.
- Send audit records to existing SOAR or SIEM tooling for log analysis and threat mitigation.
Automation and Integration
Automate and integrate DSG processes to enhance efficiency:
- Use APIs to connect DSG tools with data lakes, warehouses, and pipelines.
- Automate compliance reporting and remediation to reduce manual effort and error.
- Integrate your policy orchestration tool with existing Identity Providers.
- Leverage user attributes and data attributes for dynamic policy administration; when attributes change, access is automatically updated.
- Add classification and policy creation into data pipelines.
- Integrate automatic access provisioning into existing user access request workflows.
Enabling Encryption and Masking
Secure sensitive data with advanced techniques. For highly sensitive data, encrypt data at rest and only allow the most privileged users the ability to decrypt. For data that poses less risk but still should be protected, use dynamic masking:
- Implement encryption to protect data at rest or data in transit.
- For maximum protection, enforce workflows that encrypt sensitive fields during ingestion into a data lake or other storage.
- Add encryption procedures to ETL processes if data cannot be encrypted during data lake ingestion.
- Use deterministic encryption to allow privileged users to decrypt data from various query tools throughout the data lifecycle.
- To minimize risk, build decryption procedures in a policy administration platform; keys are not exposed to individual users.
- Carefully plan encryption strategies to minimize exposure; use different keys for different purposes.
- Use tokenization or pseudonymization to minimize the risk of exposure while maintaining data usability.
- For less sensitive data, leverage dynamic masking.
- Use a combination of user and data attributes to ensure the proper data is masked.
STEP 5: Navigate Common Challenges with DSG Implementations
Organizations often face challenges like resistance to change, limited resources, or technical complexity.
Measure Success with DSG Metrics and KPIs
Track the effectiveness of your DSG program with measurable metrics:
- Percentage of sensitive data classified.
- Percentage of least privilege access compliance.
- Rate of access violations.
- Compliance audit pass rate.
- Reduction in unauthorized access attempts.
- Time taken to resolve data access requests.
Dashboards can provide real-time visibility into these metrics by aggregating data from multiple security tools, generating visual reports, and highlighting trends or anomalies. By offering drill-down capabilities, automated alerts, and customizable views, dashboards enable security and compliance teams to quickly identify risks, track progress against key objectives, and prioritize remediation efforts. This real-time insight supports better decision-making, facilitates regulatory compliance, and drives continuous improvement in data protection strategies.
Let Privacera Help with your DSG Implementation
A successful DSG implementation involves five key steps: understanding DSG fundamentals, laying the groundwork with a cross-functional team and infrastructure audit, defining key components like policies and access controls, implementing scalable security technologies with automation, and continuously monitoring success using KPIs and dashboards for real-time insights.
Implementing a DSG strategy can be complex, but Privacera simplifies the process. From automated policy enforcement and data classification to encryption and real-time monitoring, our platform provides the tools you need to build a robust DSG program. To see how Privacera can support your organization, request a free demo today or download our whitepaper “The Blueprint For a Data Governance Program” to learn more about the importance of data governance.






